In the world of science and everyday life, we measure all sorts of things: how heavy something is (like a backpack), how far something is (like the distance to school), how hot or cold something is (like water temperature), and even how fast something moves (like a car).
To make sense of these measurements, we use units like grams, meters, degrees Celsius, and kilometers per hour. These units help us communicate and understand exactly how much or how far something is.
But it’s not just about the numbers and units. We also need tools to measure accurately. Think of a ruler to measure length, a scale to measure weight, or a thermometer to measure temperature. These tools are like our helpers, making sure we get the right numbers.
Measuring physical quantities is like using a special language to describe the world around us. It helps scientists conduct experiments, engineers build things correctly, and even helps you bake that perfect cake!
Measurement means comparison of an unknown quantity with some known fixed quantity of the same kind.
Measurement is the process of determining the magnitude of a physical quantity such as length , time, mass, temperature etc.
Measurement consist of two parts.
- 1. Magnitude
- 2. Unit of measurement
e.g. Length of pencil is 8cm
8-The numerical part 8 is magnitude
cm- is the unit
8cm- is the measurement
Table of Contents
ToggleMeasurement Of Length
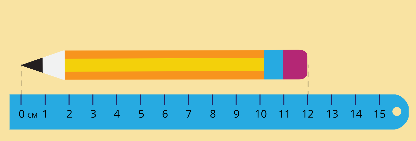
Length-Length is the distance between the two extreme ends of an object.
Instruments Used To Measure Length

Instrument of measurement-
1.Scale
2.Measuring tape
3.Vernier calipers
4.Micrometer screw gauge
- Meter rod–
- A rod made of metals like platinum and iridium is kept at the Bureau of weights and measures at Paris.
- The distance between two end marks on this rod at zero degree celcius represents a meter.
- A copy of this standard is kept in Delhi at the national Physical laboratory.(NPL)
Vernier Calliper
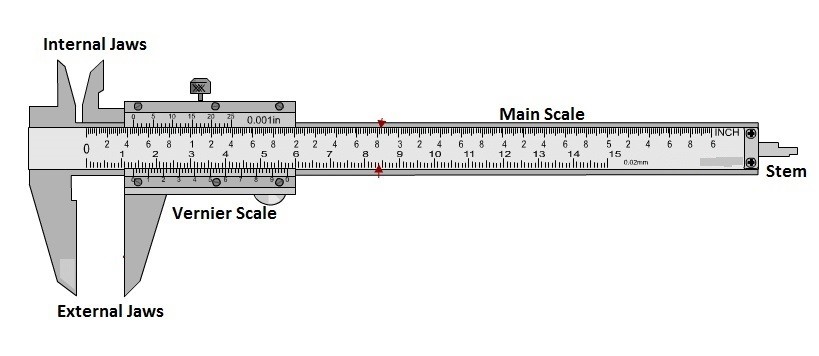
- Vernier callipers-( By Perrie Vernier in 1631)
- Very small distances are measured using Vernier callipers.
Least count– It is the smallest measurement that can be taken accurately with an instrument.
- Least count of ruler- 1 mm
- Least count of meter rod- 1 cm
- Least count of Vernier Callipers- 0.01 cm
- Least count of micrometer screw gauge- 0.001 cm
Errors in Vernier callipers–
1.Zero error of Vernier callipers- On bringing both the jaws together, if the zero mark of the Vernier scale does not coincide with the zero of the main scale then the Vernier is said to have an error. This error is known as zero error.
Types of zero error-
- Positive zero error- On bringing both the jaws together, if the zero mark of the Vernier scale is not on the right of the zero mark of the main scale, the zero error is said to be positive and the correction is to be negative.
If the positive zero error is = +y
Then the correction is = -y
- Negative zero error- On bringing both the jaws together, if the zero mark of the Vernier scale is to the left of the zero markon the main scale, the zero error is said to be negative.
If the negative zero error = -yThen the correction = +y
Micrometer Screw Gauze
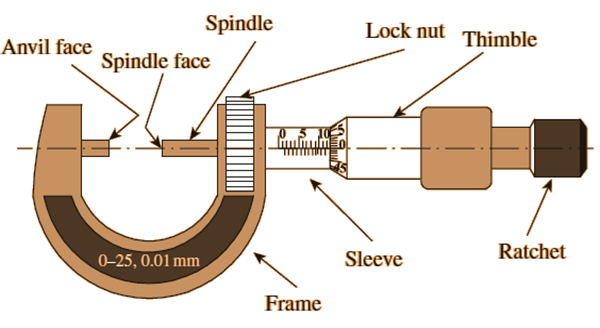
Micrometer screw gauge-Micrometer screw gauge is used to measure very small distances like thickness of paper, diameter of hair.
Least count of micrometer screw gauge- 0.001 cm.
Units Of Measuring Lengh
- Units of measuring distances–
- Light year-Light year is a unit of distance.
- One light year is the distance travelled by light in vacuum in one year.
- This unit is used in astronomy to measure the distance of stars.
- Astronomical unit(A.U.)–
- It is the average distance of the earth from the sun.
- It is used in astronomy to measure the distance of planets from the sun.
- 1 A.U. = 1.496 x 1011m
- Angstrom(A0)– The diameter of an atom is measured with the unit called Angstrom(A0).
- 1A0=10-10m
Fermi– The diameter of nucleus is measured with the help of unit Fermi.
1 Fermi= 10-15m
Measurement Of Curved Line
- Measurement of curved line-using thread 2. Using divider.
Using Thread
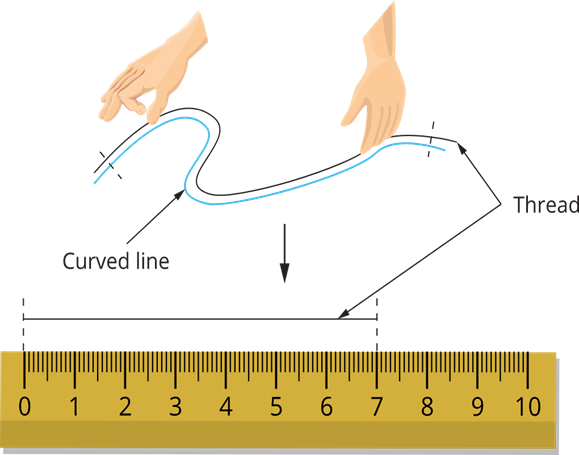
- Measuring length of curved line using thread– Match the thread with the curved line. Length of the thread is the length of the curved line.
Using Divider
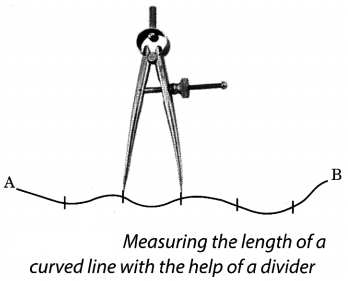
- Measuring length of curved line using divider– Take fixed distance between the legs of the divider. Count number of complete steps to cover the path of curved line. Measure the remaining distance.
- Length of curved line=( Number of complete steps x Distance between two legs of divider) + Remaining distance
Measurement Of Area
- Measurement of area– Area is the surface enclosed within the boundaries of two dimensional figure.
- Total surface possessed by an object is called its surface area or area.
- I. unit of area- square metre(m2)
- G.S. unit of area=square centimeter(cm2)
Measuring Area Of Regular Surfaces
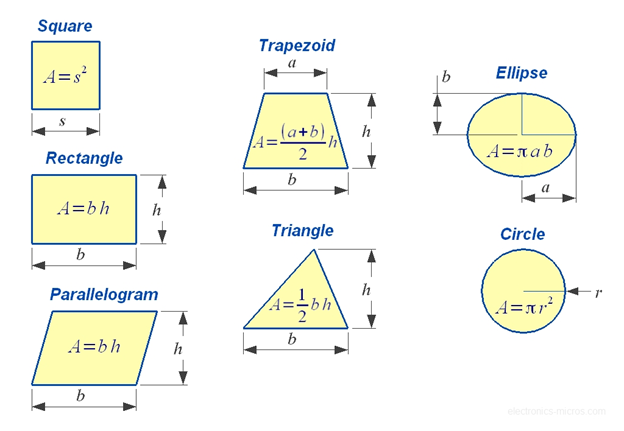
The area of regular geometrical surfaces like squares,rectangles,circles triangles is measured using specific formulae.
Area of rectangle = Length x Breath
Area of triangle= 1/2x base x height
Area of square= side x side
Area of circle= πr2(r= radius of circle)
Measuring Area Of Irregular Surfaces
Irregular shapes are those shapes that do not have equal sides and angles.
A kite, leaf, flower, etc., are examples of irregular shapes around us.
To find the area of an irregular shape, it can be divided into multiple familiar shapes, such as triangles, squares, and rectangles. Then, we can get the total area by adding the area of those smaller shapes.
Methods of finding the area of given irregular shapes.
They are:
1.Dividing the shape into possible regular polygons
2.Using the graph paper
By Dividing The Irregular Shape Into Regular Polygaons
The area of this irregular shape cannot be calculated using a single formula. Thus, we need to decompose the shape into possible simple polygons such as triangles, squares, and so on.
Therefore, the decomposed shape contains a parallelogram, rectangle, square and triangle.
So, the area of the above irregular shape can be calculated as:
Area of the shape = Area of parallelogram + Area of rectangle + Area of square + Area of triangle
Using Graph Paper
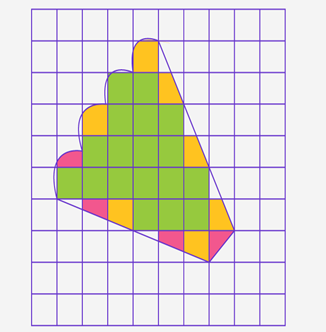
The area of irregular plane surfaces can be measured with the help of graph paper.
For fully covered square grids, we can take 1 square unit for each.
For half-covered squares, we should assign ½ square units for each.
If the square is covered more than half the portion, then assign 1 square unit for each such portion.
If the square grid is covered less than half, then assign 0 square units for each such portion.
Area of given irregular surface = 18(1) + 4(1/2) + 7(1) + 0(0)
= 18 + 2 + 7 + 0
= 27 cm²
Fully covered squares-18
Half covered squares- 3
The squares covered more than half- 7
The squares covered less than half-0
Units Of Measuring Area
S.I. unit of area- square metre(m2)
C.G.S. unit of area=square centimeter(cm2)
Larger units of area-
1 Hectare= 104 m2
1 acre= 100m2
Area of an atom or nucleus –
Area of an atom or nucleus is measured using barn
1 barn= 10-28m2
Measurement Of Volume
Volume-The space occupied by an object is called its volume.
S.I.Unit of volume is cubic meter (cu.m.)
C.G.S. unit of volume is cubic centimeter(cu.cm)
1 cubic metre = 1000 litre
Measurement Of Volume Of Regular Solids
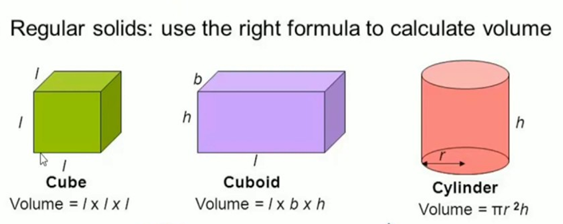
Volume of regular bodies-Volume of regular bodies is calculated using specific mathematical formula.
Volume of cube =(side)3
Volume of sphere= 4/3 π r3
Volume of cylinder= πr2h
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
Measurement Of Volume Of Irregular Solids
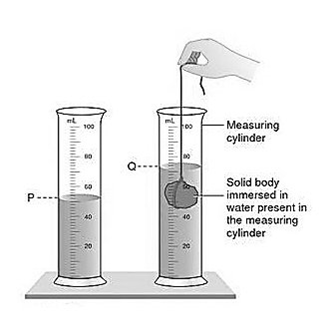
Measuring volume of irregular solids-The volume of irregular solids can be measured quite accurately by water displacement method or Archimedes Principle.
In this procedure when an object is dipped in water it displaces an amount of water that is equal to its own volume.
Water level rises when an object is dipped in water.
By taking the difference between the initial and final levels of water the volume of the object can be easily determined.
Volume of irregular solid = Final water level – Initial water level
Measuring Volume Of Liquids
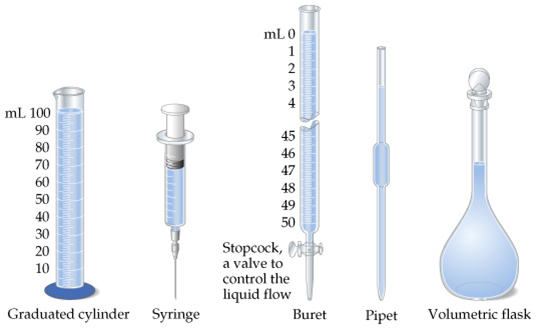
Measuring volume of liquids– The volume of liquids is measured using measuring containers.
Measurement Of Capacity

Capacity-The volume of liquid that a container can hold is called capacity of the container.
Capacity is measured in milliliter, liter.
The inner volume of a container is expressed as its capacity.
Volume of a container is greater than its capacity
Volume > Capacity
How much matter a container can hold is called its capacity.
Measurement Of Mass
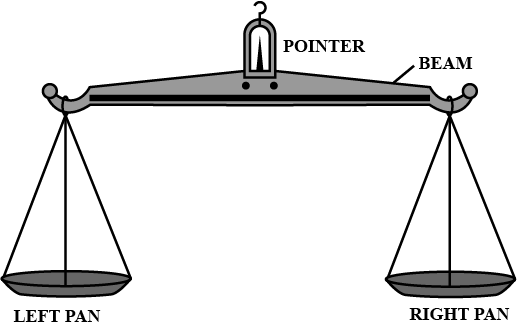
Measuring Mass:
Mass- Mass is the amount of matter contained in a body.
Mass has magnitude only. Therefore mass is a scalar quantity.
Instruments of measurement-
- Beam balance or equi-arm balance
- Physical balance
- 3. Digital weighing balance
Units Of Measurement Of Mass
Units of mass–
1g=1000mg
1kg=1000gm
S.I.unit of mass = kilogram(kg)
C.G.S.unit of mass = gram(gm)
100 kg = 1 quintal
10 quintal = 1 tonne
1 tonne = 1000kg
The largest unit of mass –
The largest unit of mass is Chandrashekhar limit or CSL.
The unit CSL is used to measure masses of stars and planets.
1 CSL = 1.4 times the mass of the Sun
The smallest unit of mass- Atomic mass unit(a.m.u.)
This unit is used to measure the mass of an atom.
1 a.m.u. = 1.67 x 10-27kg
Small weights are used to weigh costly metals like gold, silver, platinum or gems or jewels or diamonds.
1 carat = 200mg 5carat = 1gm.
Measurement Of Weight

Weight is the force with which earth pulls an object towards it. This force is called Gravity.
Weight is a vector quantity.
The weight of an object is defined as the force with which it is attracted by the earth.
The magnitude of the weight (W) is defined by the expression W = mg, where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Weight depends on gravitational force with which a body is pulled.
Weight= Mass x Gravity [ W= mg ]
Units Of Measuring Weight
S.I. unit of weight = newton or kilogram force (kgf)
C.G.S. unit of weight = dyne or gram force (gf)
Weight is measured using spring balance.
A mass of 1 kg weighs about 9.8N.
W = m x g
= 1 x 9.8 ( where g = 9.8 m/s²)
= 9.8 N
=10N
Difference Between Mass And Weight
Mass | Weight |
It is the quantity of matter contained in a body
The mass of body remains constant everywhere
It is measured using beam balance or physical balance It is measured in Kilogram or gram. It has only magnitude and no direction. Mass is a scalar quantity. | It is the force with which the body is pulled towards the earth Weight of a body changes from one place to other. It is measured using spring balance.
It is measured in Newton. It has both magnitude and direction. Weight is a vector quantity |
Gravitational force of moon = 1/6 times that of the earth.
Weight on the moon = 1/6 x Weight on earth
Gravitational force on mars = 1/ 5 times that of the earth.
Weight on mars = 1/5 x weight on the earth
Measurement Of Temperature
Temperature – The hotness or coldness of a body is called temperature
Instrument of measurement of temperature- Thermometer is used to measure temperature.
S.I. unit of temperature– kelvin (K)
C.G.S.Unit– Celsius
The Fahrenheit Scale is also used to measure temperature.
Temperature Scales
Temperature scales-
- Celsius scale
- 2. Fahrenheit scale
- 3. Kelvin scale
Celsius scale- 100 divisions ( 00C to 100 0C)
Celsius thermometer was invented by Swedish astronomer Ander Celcium in 1701-1744.
The graduation on a Celsius thermometer are from 00C to 100 0C.
There are 100 divisions between 00C to 100 0C.
Fahrenheit scale- 180 Divisions ( 320F to 2120F)
The Fahrenheit scale was Invented by German physicist Daniel Fahrenheit in 1686-1736.
The graduation on this thermometer are from 320F to2120F.
The number of divisions between these two points are 180.
Kelvin scale- It is a theoretical scale in which the value can be obtained simply by adding 273 to the Celsius Scale.
Kelvin scale= Celsius scale + 273
00c = 273 k 1000c=100 +273 =373K
Relation Between Different Temperature Scales
Relation between Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale and Kelvin scale-
1.Conversion of 0C to 0F 0F = (0C x(9/5)) + 32
2.Conversion of 0F to 0C C= (F-32) x 5/9
3.Conversion of 0C to K- K = 0C + 273
Celsius scale and Fahrenheit scale are equal at -40.
Freezing point of water– 00C = 320F = 273K
Boiling point of water- 1000C = 2120 F =373K
Normal human body temperature- 370C = 98.40F = 310K
The Fahrenheit Scale is more accurate than Celsius scale.
Absolute Zero Temperature
Absolute zero occurs at a temperature of 0 degrees Kelvin, or -273.15 degrees Celsius, or at -460 degrees Fahrenheit.
Absolute zero = 0K = 273.150C = -4600F
Absolute zero is the lowest temperature possible. At a temperature of absolute zero there is no motion and no heat.
The particles present at this temperature will be constant and do not move, this is the condition of freezing.
Absolute zero is the temperature at which all gases exist in their liquid state.
This temperature range can be achieved theoretically not practically.
Liquids Used In Thermometers
Alcohol-Alcohol is used as a thermometric liquid in certain situations because
1.The freezing point of alcohol is less than -100°C, so we can measure very low temperature using an alcohol thermometer.
2.The expansion of alcohol is more than that of mercury for the same rise or fall of temperature, hence alcohol thermometer can measure temperature more accurately.
3.It’s a bit cheaper than mercury.
4.The bright color of alcohol makes it easy to see on the glass capillary tube.
5.Unlike mercury, alcohol is less toxic and will evaporate away quickly if subjected to high temperatures. Therefore, it is used to measure low temperatures.
6.It is Unharmful to humans and the environment
7.Freezing point of alcohol is -1120c.Hence temperatures below -1120 c can be measured.
8.It is used to study weather conditions and atmosphere
Mercury-Mercury is used in thermometer because
1.Melting point of mercury is -390c and boiling point is3570c.
2.Therefore large range temperatures can be measured using mercury thermometer .
3.Mercury is used in thermometer because
4.It is shiny metal and can be easily seen through glass.
5.It expands and contracts uniformly.
6.It does not stick to the glass.
7.It does not freeze or vaporize easily.
Types Of Thermometers
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Laboratory Thermometer
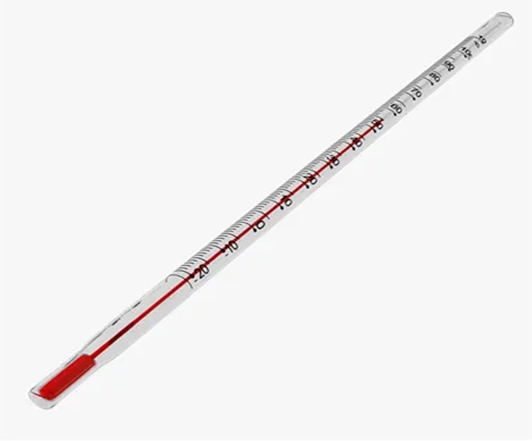
It is used in laboratories.
Markings on its scale are from -100c to 1100c.
Laboratory thermometers are designed to measure boiling points, freezing points, and temperatures of various substances.
The range of a laboratory thermometer is -10°C to 110°C. Hence, it can measure readings even below 0°C till -10°C. It can also measure the temperature of 100°C.
Clinical Thermometer
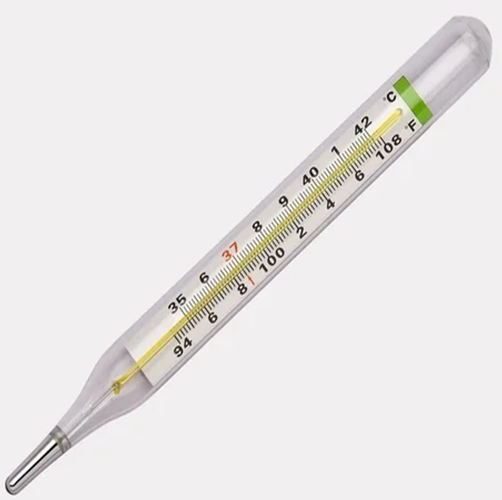
Clinical thermometer is used to measure body temperature.
Markings on clinical thermometer are from 350c to 420c(950F to 1100F) or ( Normal human body temperature is 370c or 98.40F)
It is a long narrow glass tube with a bulb containing mercury at the end..
The normal human body temperature is 37˚C, which can fluctuate between the ranges 35˚C to 42˚C. Hence, the clinical thermometers range from 35˚C to 42˚C.
The level of mercury tells our body temperature in ˚C.
Since mercury is a toxic element, thus these thermometers have been replaced by digital thermometers nowadays.
Maximum -Minimum Thermometer

Working of maximum and minimum thermometer:
When the temperature increases, the alcohol in the left tube expands.
This causes the mercury to move towards the right tube.
A metal indices on the right tube also shifts which gives us the maximum temperature for that day.
When the temperature decreases, the alcohol contracts in the left tube and the mercury moves into the left tube.
A metal indices in the left tube shift and give us the minimum temperature of the day.
It is also commonly known as a maximum–minimum, minimum–maximum, maxima–minima or minima–maxima thermometer,
Measurement Of Time
Time- The interval between two events is called time.
S.I. unit of time- second(s)
C.G.S. unit of time- second(s)
Other units of time measurement
Minute=60 second
1 hour = 60 minute
Day-24 Hours/ 2×12 hours
Week-7 days
Fortnight- 2 weeks
Month- 28,29,30,31 days
Year- 12 months, 365/366 days, 52 weeks+ 1,2 days
Quarter-3 months
Olympiad-4 years
Decade- 10 years
Century-100 years
Millennium-1000 years
Epoch- composed of millions years
Period- composed of Epochs
Era- composed of Periods
Eon- composed of Eras
Instruments Of Measurement Of Time

Water clock- It was made by Egyptians. It measure time as water dripped from one part to another.
Sundial- It consist horizontal circular board divided into 12 triangular parts. It works only when sun is shining. Still exist in India at Jantarmantar in Delhi and Jaipur built by Mirza raje jaysingh.
Hour glass or sand clock– In a sand glass sand flows from one container to another through a small hole connecting them.
Atomic clock– Used to measure very short time intervals.
Digital stop watch- Used to measure short time intervals of minutes and seconds
Analogue stop watch- Used to measure time intervals of minutes and seconds
Watch- used to measure time intervals of hours minutes and seconds.
Radioactive decay clock- Used to measure long time intervals of years to thousands of years
Silver jubilee – For a 25th anniversary
Ruby jubilee – for 40thanniversary
Golden Jubilee – for 50th anniversary
Diamond Jubilee – for 60th anniversary
Sapphire jubilee – For 65th anniversary
Platinum jubilee – for 70th anniversary
Double platinum jubilee – for 75th anniversary
Centenary – for 100 th anniversary
Measurement Of Density
Density- The mass of unit volume of a substance is called density.
Density = Mass /Volume
S.I. unit of density is kilogram per cubic meter(kg/m3)
C.G.S. unit of density is gram per cubic centimeter( gm/cm3)
Density is a scalar quantity.
Density is mass per unit volume.
As volume increases the density decreases on the other hand as volume decreases the density increases
Measurement Of Relative Density

Relative density– The relative density of a substance is the ratio of density of the substance to the density of water at 40c.
Relative density is also called specific mass or specific gravity.
Relative density has no units as is ratio of two densities.
Relative density is measured using Relative Density Bottle.
Conclusion
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
